Managing diabetes involves keeping your blood sugar levels in check to lead a healthy life. One helpful way to do this is through the “pinch method for diabetes.” This technique offers a less uncomfortable and more straightforward approach to monitor your blood sugar levels.
Instead of using traditional pricking methods, the pinch method involves gently pinching a part of your finger to get a small blood sample. This method matters because it’s easier on you and ensures consistent monitoring, which is vital for managing diabetes effectively. Let’s delve into how the pinch method works and why it’s a valuable tool in your diabetes management toolbox.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
When it comes to diabetes management, keeping an eye on your blood sugar levels is essential. There are various methods available, and the “pinch method for diabetes” is one of them, offering a simpler way to keep track. Let’s explore how this method works and its benefits.
The Pinch Method for Diabetes
The pinch method is a user-friendly way to monitor blood sugar levels for individuals with diabetes.
This technique offers a less uncomfortable experience compared to traditional finger-prick methods. Let’s dive into the details of how the pinch method works and why it’s advantageous.
What is the Pinch Method for Diabetes?
The pinch method involves gently pinching a soft area on your finger to enhance blood flow to the surface.

This increased blood flow makes it easier to collect a small blood sample for testing. Unlike using a needle to prick the fingertip, the pinch method aims to be less painful and more approachable.
Performing the Pinch Method
- Prepare: Before testing, ensure your hands are clean to prevent any potential infections.
- Choose a Testing Site: Opt for a fleshy area on your finger, such as the sides or the soft part.
- Gently Pinch: Using your thumb and forefinger, gently pinch the chosen area. Apply slight pressure to encourage blood circulation.
- Collect the Sample: Once blood flow increases, use a blood glucose monitor to gather the blood sample. Follow the monitor’s instructions for accurate testing.
Advantages of the Pinch Method
The pinch method for monitoring blood sugar levels offers several benefits compared to traditional finger-prick methods. Let’s explore these advantages in detail.
1. Reduced Discomfort
Traditional finger-prick methods involve a needle puncturing the fingertip, which can be uncomfortable and even painful for some individuals.
The pinch method, on the other hand, involves gently pinching the skin. This approach is associated with less discomfort, making blood sugar testing a more tolerable experience.
Read Also: Preventions for Diabetes and Complications in Male
2. Smaller Blood Sample
The pinch method requires only a small blood sample for testing. This is especially advantageous for individuals who may feel anxious about providing larger blood samples.
The smaller sample size is still sufficient for accurate blood sugar readings, but it can ease concerns for those who worry about the amount of blood needed.
3. Needle Apprehension
For individuals with a fear of needles, the pinch method presents a more approachable alternative.
Since it doesn’t involve a needle piercing the skin, it can help reduce anxiety and make the process of blood sugar monitoring less daunting.
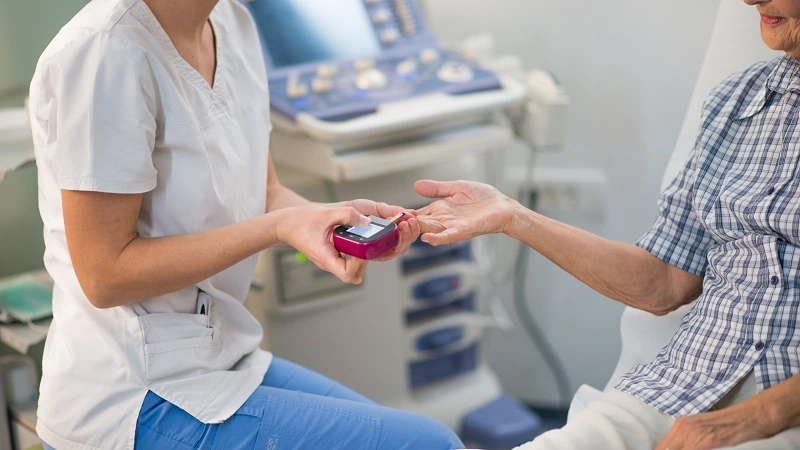
4. User-Friendly Process
The pinch method is designed to be user-friendly. The steps are simple to follow, involving just the gentle pinch of a chosen area on the finger and using a blood glucose monitor.
This straightforward approach makes it accessible to individuals of all experience levels, including those who might be new to diabetes management.
5. Minimally Invasive
The pinch method is considered minimally invasive because it doesn’t involve puncturing the skin with a needle. Instead, it focuses on enhancing blood flow through gentle pressure.
This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with sensitive skin or those prone to skin irritation.
6. Convenience and Accessibility
The simplicity of the pinch method means that it can be easily incorporated into daily routines. Whether at home or on the go, the pinch method enables you to monitor your blood sugar levels with relative ease, helping you stay on track with your diabetes management plan.
Tips for Successful Blood Sugar Testing
To ensure accurate results and effective diabetes management, here are some essential tips for successful blood sugar testing using the pinch method.
1. Clean Hands for Accuracy
Before performing the pinch method, always make sure to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
This helps remove any dirt, oils, or contaminants that could affect the accuracy of your blood sugar reading.
2. Choose the Right Site
Select a suitable testing site on your finger, preferably on the sides or the fleshy part. Avoid areas with calluses, scars, or wounds, as these can impact the accuracy of the test and cause discomfort.
3. Gentle Pressure
When pinching the chosen area, apply gentle pressure. The goal is to enhance blood flow to the surface without causing undue discomfort. Avoid squeezing too hard, as this could result in excessive pain or bruising.
4. Monitor Consistency
Test your blood sugar at the recommended times, such as before meals, after meals, and as directed by your healthcare provider. Consistency in testing helps you and your healthcare team track your progress accurately.
5. Proper Blood Glucose Monitor Usage
Familiarize yourself with the instructions for your blood glucose monitor. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for applying the blood sample to the test strip and interpreting the results. This ensures reliable and precise readings.
6. Record Your Readings
Keep a log of your blood sugar readings. Recording your results over time allows you and your healthcare provider to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
7. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water can help ensure reliable blood flow, which is crucial for obtaining accurate blood samples. Proper hydration supports consistent and dependable results during testing.
8. Avoid Rushing
Take your time when performing the pinch method. Rushing can lead to errors in blood collection or testing, potentially affecting the reliability of your results.
9. Monitor for Any Changes
Be attentive to any changes in your skin or the sensation of your fingers. If you notice any unusual signs, such as redness, swelling, or pain, consider changing the testing site and consult your healthcare provider if necessary.
10. Seek Guidance
If you’re unsure about any aspect of the pinch method or blood sugar testing, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or diabetes educator.
They can provide personalized guidance to ensure you’re using the pinch method effectively.
Conclusion
Incorporating the pinch method for diabetes management offers a comfortable and accessible way to monitor blood sugar levels.
By gently stimulating blood flow and obtaining a small sample, this technique reduces discomfort, anxiety, and the need for larger blood samples.
The advantages of minimal invasiveness, reduced pain, and user-friendliness make the pinch method a valuable tool in your diabetes care routine.
Consistent monitoring empowers you to make informed decisions about your health and work closely with your healthcare team for optimal management.
Remember, this method provides a bridge to effective diabetes management without compromising your comfort.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Is the pinch method suitable for everyone?
The pinch method is generally suitable for most individuals with diabetes. However, consult your healthcare provider to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific situation.
2. Can I use the pinch method if I have sensitive skin?
Yes, the pinch method’s gentle approach makes it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin. Still, choose testing sites wisely to avoid discomfort.
3. How often should I test my blood sugar using the pinch method?
Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Common times include before meals, after meals, and occasionally at other intervals.
4. Can I use the pinch method with a continuous glucose monitor (CGM)?
The pinch method is typically used with traditional blood glucose monitors. Consult your healthcare provider regarding its compatibility with CGMs.
5. Does the pinch method provide accurate results?
Yes, when performed correctly, the pinch method offers accurate blood sugar readings. Follow proper technique and monitor consistently.
6. What if I’m not getting enough blood for the test?
Gently massage the chosen site to encourage blood flow. If difficulties persist, consider an alternative site and consult your healthcare provider if needed.
7. Is the pinch method covered by insurance?
Check with your insurance provider regarding coverage for blood glucose monitoring supplies, including test strips for the pinch method.
8. Can children use the pinch method?
Children can use the pinch method with proper supervision. Work closely with pediatric healthcare professionals for guidance.
9. Are there any risks associated with the pinch method?
When done correctly, the pinch method is generally safe. However, consult your healthcare provider if you experience any unusual reactions or discomfort.
Medical References
- American Diabetes Association. (2020). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 43(Supplement 1), S14-S31.
- International Diabetes Federation. (2019). Managing Older People with Type 2 Diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.idf.org/e-library/guidelines/150-global-guideline-for-managing-older-people-with-type-2-diabetes.html
- American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. (2015). Comprehensive Type 2 Diabetes Management Algorithm. Endocrine Practice, 21(4), 438-447.
- American Diabetes Association. (2017). Microvascular Complications and Foot Care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 40(Supplement 1), S88-S98.
- Heinemann, L., Freckmann, G., & Alsalim, W. (2012). Different commercial blood glucose meters fulfill ISO 15197 in spite of different hematocrit ranges. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 28(4), 595-603.
- American Diabetes Association. (2021). 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care, 44(Supplement 1), S111-S124.